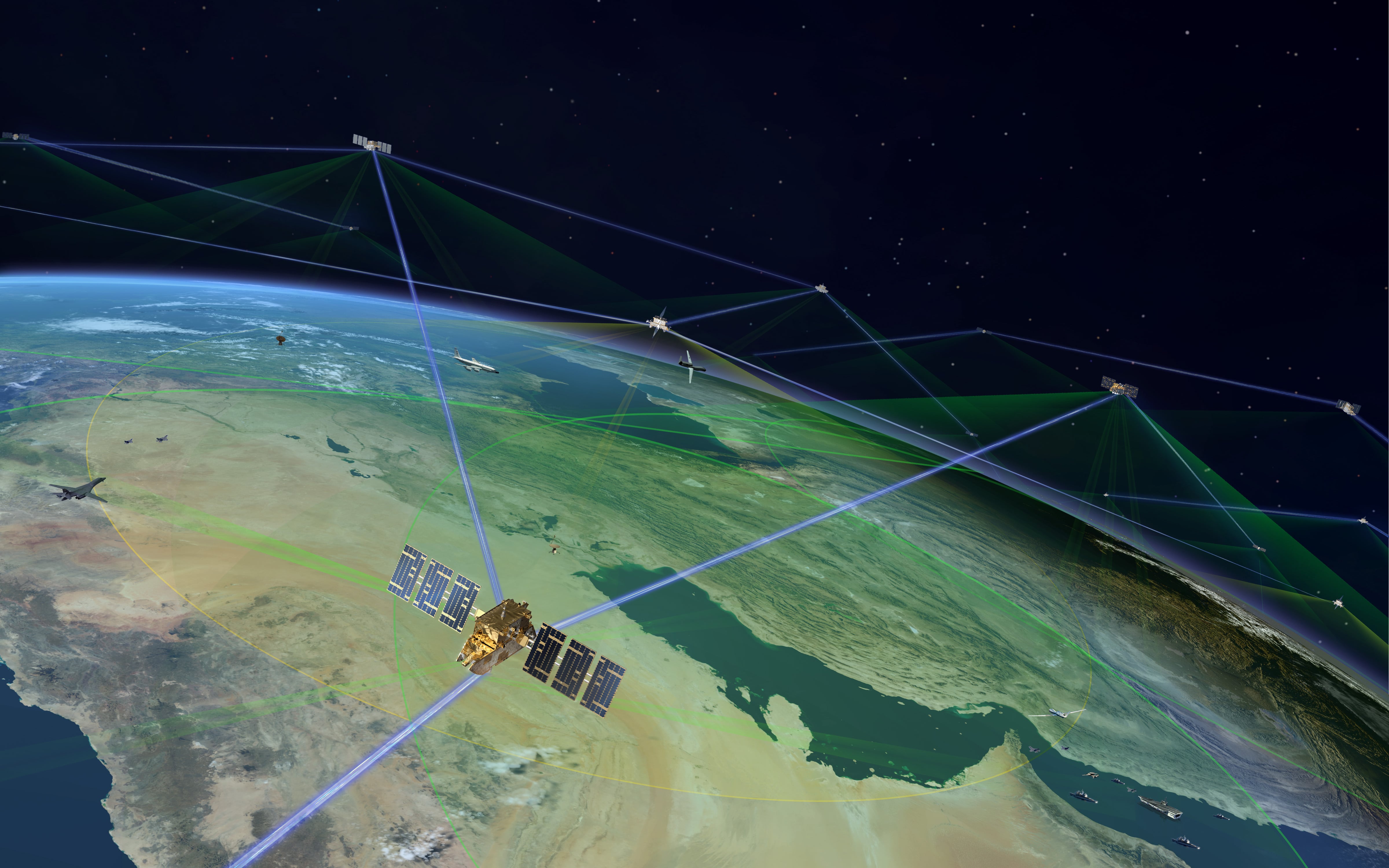
Drones are everywhere in the Pentagon today. While unpeopled vehicles are most closely associated with the Air Force and targeted killing campaigns, remotely controlled robots are in every branch of the military and used across all combatant commands. The fiscal year 2018 defense authorization contained the largest budget for drones and robots across the services ever, a sign of just how much of modern warfare involves these machines.
Which is perhaps why, when the Department of Defense released its latest roadmap for unmanned systems, the map came in at a punchy 60 pages, far shy of the 160-page tome released in 2013. This is a document less about a military imagining a future of flying robots and more about managing a present that includes them.
The normalization of battlefield robots
Promised since at least spring 2017, the new roadmap focuses on interoperability, autonomy, network security and human-machine collaboration.
The future of drones, and of unpeopled ground vehicles or water vehicles, is as tools that anyone can use, that can do most of what is asked of them on their own, that communicate without giving away the information they are sharing, and that will work to make the humans using the machines function as more-than-human.
This is about a normalization of battlefield robots, the same way that mechanized warfare moved from a theoretical approach to the standard style of fighting by nations a few generations ago. Network security isn’t as flashy a highlight as “unprecedented battlefield surveillance by flying robot,” but it’s part of making sure that those flying cameras don’t, say, transmit easily intercepted data over an open channel.
“Future warfare will hinge on critical and efficient interactions between war-fighting systems,” states the roadmap. “This interoperable foundation will transmit timely information between information gatherers, decision makers, planners and war fighters.”
A network is nothing without its nodes, and the nodes that need to be interoperable here are a vast web of sensors and weapons, distributed among people and machines, that will have to work in concert in order to be worth the networking at all. The very nature of war trends toward pulling apart networks, toward isolation. Those nodes each become a point at which a network can be broken, unless they are redundant or autonomous.
Where will the lethal decision lie?
Nestled in the section on autonomy, the other signpost feature of the Pentagon’s roadmap, is a small chart about the way forward. In that chart is a little box labeled “weaponization,” and in that box it says the near-term goals are DoD strategy assessment and lethal autonomous weapon systems assessment.
Lethal autonomous weapon systems are of such international concern that there is a meeting of state dignitaries and humanitarian officials in Geneva happening at the exact moment this roadmap was released. That intergovernmental body is hoping to decide whether or not militaries will develop robots that can kill of their own volition, according to however they’ve been programmed.
The Pentagon, at least in the roadmap, seems content to wait for its own assessment and the verdict of the international community before developing thinking weapons. Hedging on this, the same chart lists “Armed Wingman/Teammate (Human decision to engage)” as the goal for somewhere between 2029 and 2042.
“Unmanned systems with integrated AI, acting as a wingman or teammate with lethal armament could perform the vast majority of the actions associated with target identification,tracking, threat prioritization, and post-attack assessment," reads the report.
"This level of automation will alleviate the human operator of task-level activities associated with the engagement of a target, allowing the operator to focus on the identified threat and the decision to engage.”
The roadmap sketches out a vision of future war that hands off many decisions to autonomous machines, everything from detection to targeting, then loops the lethal decision back to a human responsible for making the call on whether or not the robot should use its weapons on the targets it selected.
Humans as battlefield bot-shepards, guiding autonomous machines into combat and signing off on the exact attacks, is a possible future for robots in war, one that likely skirts within the boundaries of still-unsettled international law.
Like its predecessor, this drone roadmap is plotting a rough path through newly charted territory. While it leans heavily on the lessons of the present, the roadmap doesn’t attempt to answer on its own the biggest questions of what robots will be doing on the battlefields of tomorrow. That is, fundamentally, a political question, and one that much of the American public itself doesn’t yet have strong feelings about.
Kelsey Atherton blogs about military technology for C4ISRNET, Fifth Domain, Defense News, and Military Times. He previously wrote for Popular Science, and also created, solicited, and edited content for a group blog on political science fiction and international security.