Editor’s note: This story was updated on Oct. 15 at 9:55 a.m. EST with additional information.
Within hours of the horrific attack by Hamas, the U.S. began moving warships and aircraft to the region to be ready to provide Israel with whatever it needs to respond.
A second U.S. carrier strike group departs from Norfolk, Virginia, on Friday. Scores of aircraft are heading to U.S. military bases around the Middle East. Special operations forces are now assisting Israel’s military in planning and intelligence. The first shipment of additional munitions has already arrived.
[Israel-Hamas war misinformation flourishes on X as platform struggles]
More is expected, soon. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin will arrive in Israel Friday to meet with Israeli leaders to discuss what else the U.S. can provide.
For now, the buildup reflects U.S. concern that the deadly fighting between Hamas and Israel could escalate into a more dangerous regional conflict. So the primary mission for those ships and warplanes is to establish a force presence that deters Hezbollah, Iran or others from taking advantage of the situation. But the forces the U.S. sends are capable of more than that.
A look at what weapons and options the U.S. military could provide:
Missiles for Iron Dome
The U.S. is providing some personnel and much-needed munitions to Israel. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin announced that a small special operations cell was now assisting Israel with intelligence and planning, and providing advice and consultations to the Israeli Defense Forces on hostage recovery efforts. However those forces have not been tasked with hostage rescue, which would put them on the ground fighting in the conflict. That’s something the Biden administration has not approved and White House spokesman John Kirby has said the Israelis do not want.
The U.S. is also getting U.S. defense companies to expedite weapons orders by Israel that were already on the books. Chief among those are munitions for Israel’s Iron Dome air defense system.
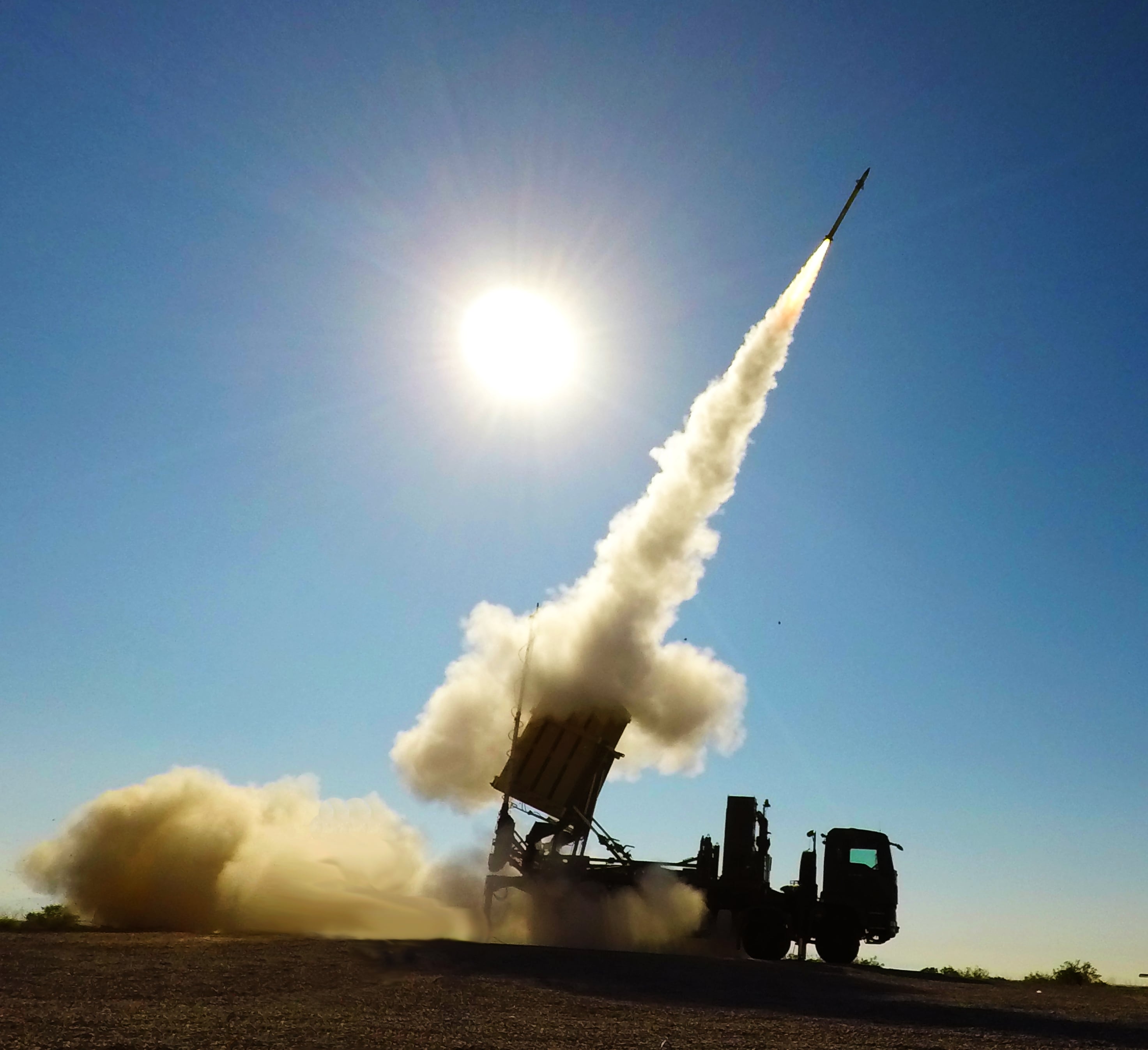

“We’re surging additional military assistance, including ammunition and interceptors to replenish Iron Dome,” President Joe Biden said Tuesday. “We’re going to make sure that Israel does not run out of these critical assets to defend its cities and its citizens.”
Iron Dome’s missiles target rockets that approach its cities. According to Raytheon, Israel has 10 such systems in place. Beginning with Saturday’s attack, Hamas has fired more than 5,000 rockets at Israel, most of which the system has been able to intercept, according to the Israel Defense Forces.
Raytheon produces most of the missile components for Iron Dome in the U.S., and the Army has two systems in its stockpile.
The Iron Dome munitions the U.S. provides to Israel will likely be above and beyond what Israel has ordered and will be part of ongoing military assistance packages. Those packages will also include small diameter bombs and JDAM kits — essentially a tail fin and navigation kit that turns a “dumb” bomb into a “smart” bomb and enables troops to guide the munition to a target, rather than simply dropping it.
Ships and aircraft
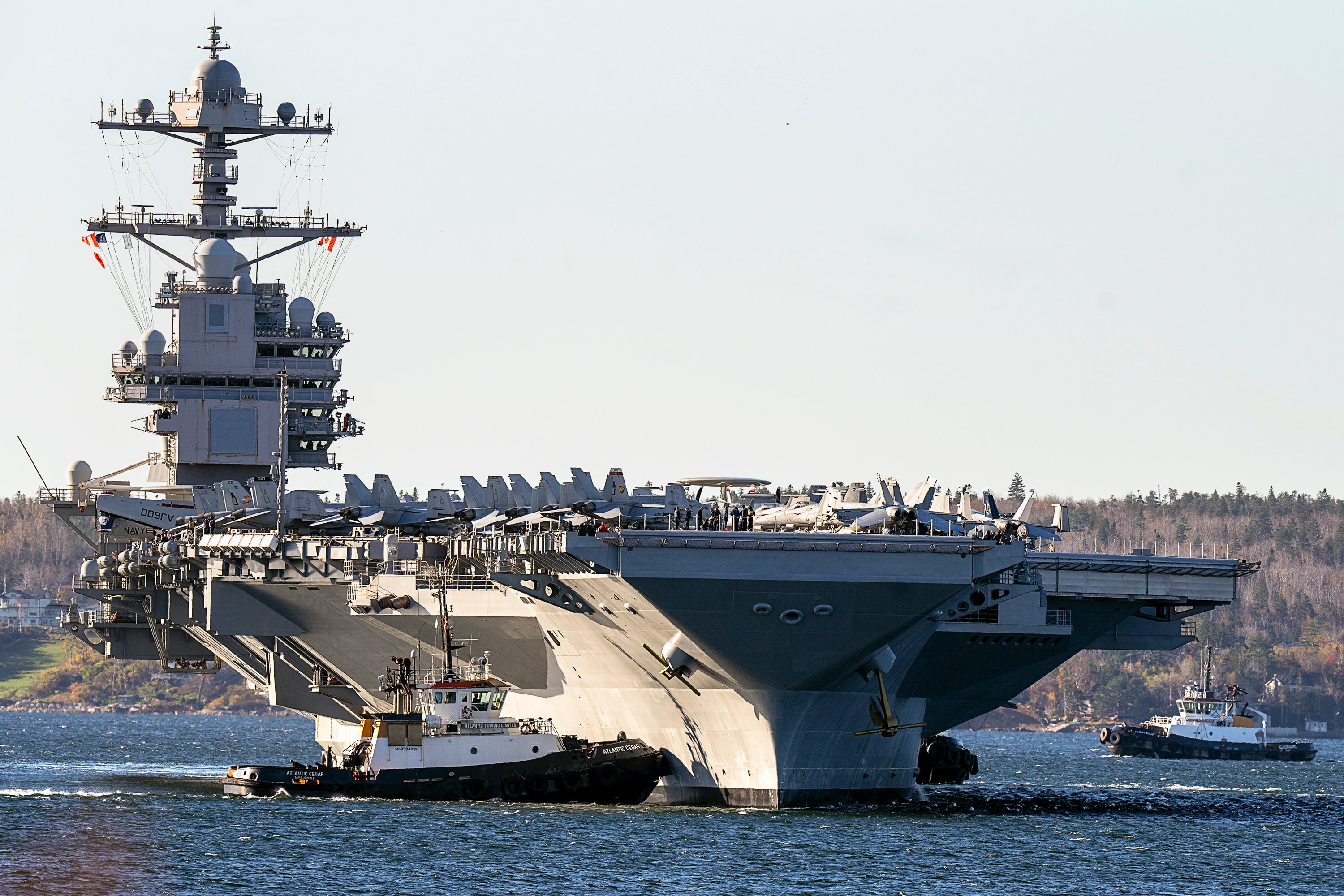
One of the most visible examples of the U.S. response was the announcement Sunday by the Pentagon to redirect the Gerald R. Ford carrier strike group to sail toward Israel. The carrier had just completed an exercise with the Italian Navy when the ship and its crew of about 5,000 were ordered to quickly sail to the Eastern Mediterranean.
One week after the attacks, as Israel positioned for a major ground offensive into Gaza City, Austin announced a second carrier group would be sailing toward Israel, as he ordered the USS Dwight D. Eisenhower carrier strike group to join the Ford in the Eastern Mediterranean. In a statement announcing the move, Austin said he was sending the Eisenhower too “as part of our effort to deter hostile actions against Israel or any efforts toward widening this war following Hamas’s attack on Israel.”
The carriers provide a host of options. They serve as primary command and control operations centers and can conduct information warfare. They can launch and recover E2-Hawkeye surveillance planes, recognizable by their 24-foot (7-meter) diameter disc-shaped radars. The planes provide early warnings on missile launches, conduct surveillance and manage the airspace, not only detecting enemy aircraft but also directing U.S. movements.
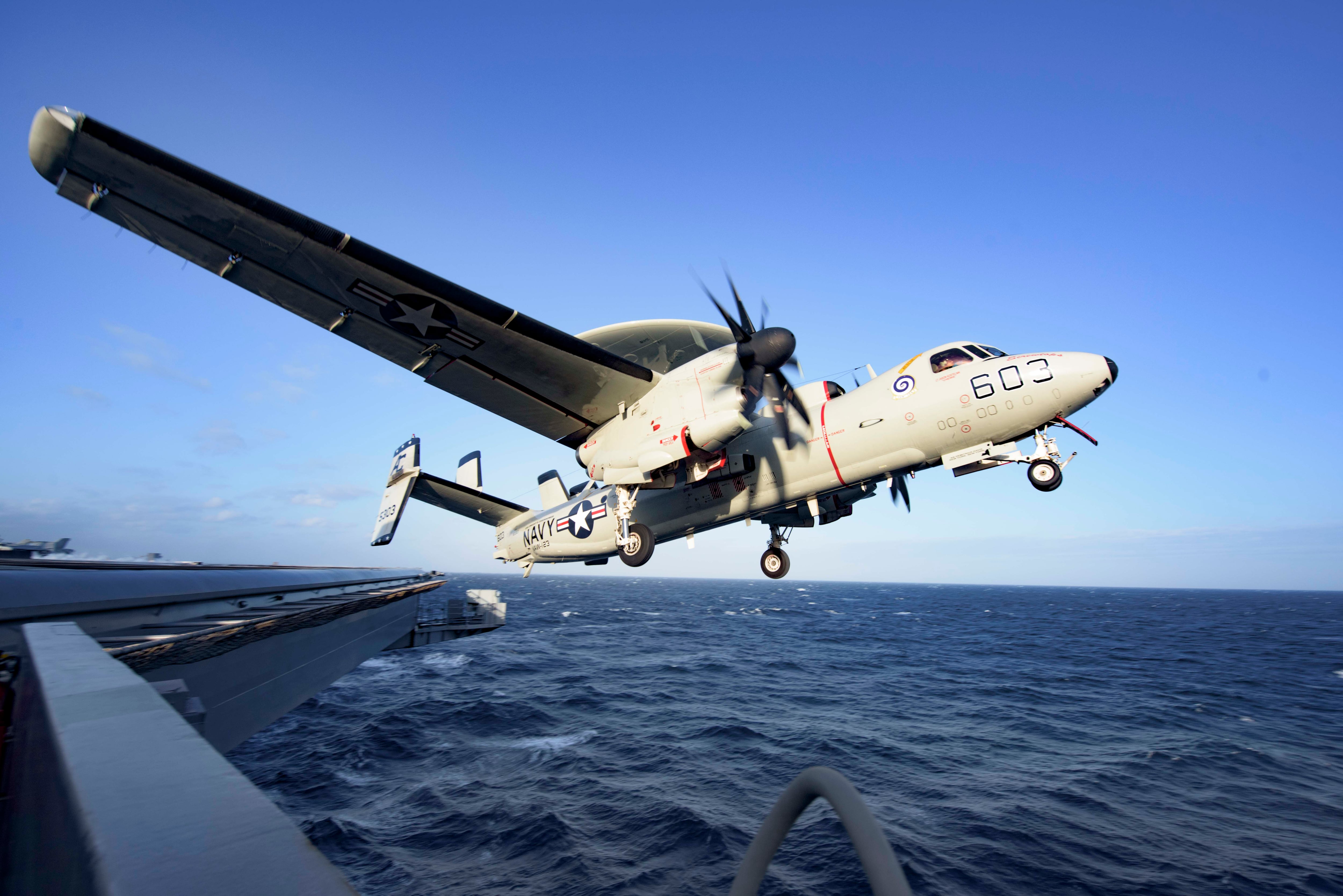

They also serve as a floating airbase for F-18 fighter jets that can fly intercepts or strike targets. And the carriers can flex to provide significant capabilities for humanitarian work, including onboard hospitals with ICUs, emergency rooms, medics, surgeons and doctors. They also sail with helicopters that can be used to airlift critical supplies in or victims out.
The Eisenhower had already been scheduled to deploy to the Mediterranean on a regular rotation, and the Ford is near the end of its scheduled deployment. But the Biden administration for now has decided to have both carriers there.
Air Force action
The Pentagon has also ordered additional warplanes to bolster existing squadrons of A-10, F-15 and F-16 squadrons at bases throughout the Middle East and is ready to add more if needed.
Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall said Tuesday at an Atlantic Council event that the service was doubling up by directing units that were about to come home to remain in place and stay there along with their replacements.

The U.S. Air Force already has significant airpower in the region to conduct manned and unmanned operations, most notably in Syria where an Air Force F-16 last week was ordered to shoot down a Turkish drone that was posing a threat to U.S. ground forces operating there.
Kendall also said U.S. Air Force C-17s have landed in and departed from Israel since the attacks. The transport planes were picking up U.S. military personnel who were there for a military exercise that hadn’t started yet when the attacks began, the Air Force said in a statement.
Neither the Air Force nor Central Command would comment on what additional missions U.S. airpower might take on in response to the conflict.
Associated Press writer Colleen Long contributed to this report.
Tara Copp is a Pentagon correspondent for the Associated Press. She was previously Pentagon bureau chief for Sightline Media Group.