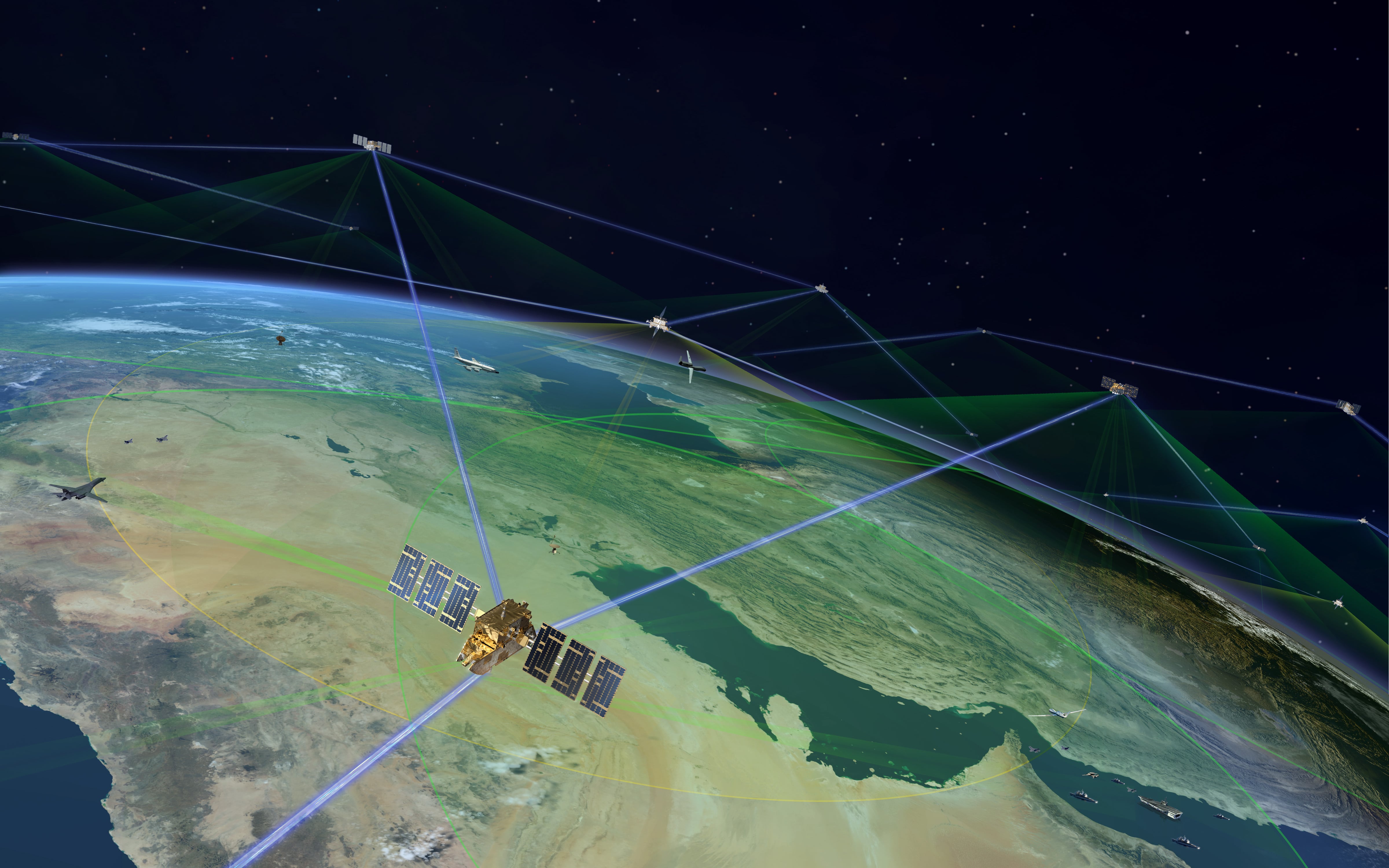
Every military force around the world wants to develop and enhance cyber power projection, and the U.S. military is no exception. Each branch has established a cyber capability and continues to enhance and refine those capabilities. Given the relative absence of tested, tried and true approaches to cyber power projection, developing a strategy in support of the cyber mission has many people a bit uneasy, and for good reason.
In November 2012, the U.S. Navy produced a document titled Navy Cyber Power 2020. The objective was to create and sustain an advantage in cyber domain, a very tall order given the rapid and continuous change that is taking place in offensive and defensive cyber operations. Consider all the devices, computers, connected equipment and networks that are on board the 272 deployable ships.
Resource: Navy Cyber Power 2020
The Navy has a wide range of cyber capabilities, including cryptology, signals intelligence, cyber, electronic warfare, information operations, intelligence, networks, and even has some aspects of its assets and abilities in space. As one might expect these capabilities are constantly being evaluated, refined and enhanced as is required to keep pace with the changing evolution of connected technology and the ever increasing threat from a broad range of adversaries including non-nation states. We all recognize that the current pace of technological advancement is very rapid and moving to warp-speed. That alone more than justifies the increased efforts of the Navy and the rest of the U.S. Department of Defense to research and develop new advanced technologies that has important capabilities to the military.
Defining the future capabilities is necessary for dominance in cyber power projection and is an extremely challenging undertaking. There is little doubt that this requires a true commitment and long-term funding. Clearly, time is running out and the race is on. The U.S. Navy or the U.S. military in general must aggressively work to slow and reverse the erosion of U.S. military superiority, whether perceived or real. In addition, they must continuously enhanced cyber capabilities. This is mandatory, and all of this requires new technology to ensure superiority in cyber warfare.
Another interesting document is The PLA Navy – New Capabilities and Missions for the 21st Century, which pertains to China's Peoples' Liberation Army Navy. While Navy Cyber Power 2020 established an ambitious agenda, is it really aggressive enough to keep up with the pace of technological advancement that is currently taking place? When you examine "The PLA Navy" you get a picture of how a potential adversary will integrate technology into every aspect of their strategy going forward.
Resource: The PLA Navy
If you examine what has recently been published about the Navy's advanced technology initiatives, you get just a glimpse of what they have going on. When you stretch your imagination and get creative, you may be able to think about the classified side of technology initiatives that are likely to be underway behind the closed doors of classified research labs across the United States. You can bet some of those labs are focused on cyber capabilities such as irregular warfare, information dominance, systems survivability, cyber integration into power projection and of course defense of Navy technology systems.
The U.S. has a rich history of technology dominance. As talented as our researchers are we are in global technological competition. Several influential thinkers have expressed deep concerns about the United States' ability to maintain technological dominance and have pointed to several pieces of supporting information. While the decrease in the U.S. defense budget is one aspect, the growing shortage of STEM graduates is another. Another deeply concerning aspect of the immediacy of this issue was documented in an Accenture study that put the United States fifth behind the Netherlands, Japan, Germany and China in innovation.
Technological supremacy is a national security issues and that impacts ever part of our military and intelligence organizations. After weighing the evidence before us one thing is certain: We do not want to fall any further behind; so immediate and decisive actions are necessary.